Prostate cancer surgery
For many people, surgery will be a suggested treatment option. It is worth discussing with your urologist or treating doctor whether there are other options, such as radiation therapy, available to you.
The main type of surgery for localised and locally advanced prostate cancer is a radical prostatectomy.
Learn more about:
- What types of surgery are there?
- How the surgery is done
- Radical prostatectomy to remove the prostate
- Making decisions about surgery
- What to expect after surgery
What types of surgery are there?
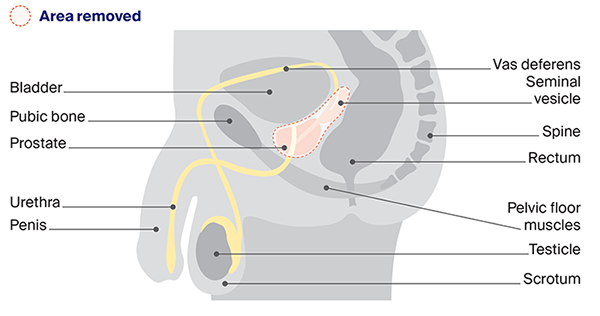
Radical prostatectomy involves removes all the prostate, part of the urethra and the seminal vesicles. The urethra is rejoined to the bladder, and the vas deferens (that carry sperm from the testicles to the penis) will be sealed.
Some people have a nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy, to avoid damaging the nerves that control erections. This is only for lower-grade cancers where the cancer isn’t close to these nerves, and it works best for those who had strong erections before diagnosis. Problems with erections are common even with nerve-sparing surgery.
Cancer cells can spread from the prostate to nearby lymph nodes. For intermediate-risk or high-risk prostate cancer, nearby lymph nodes may also be removed (pelvic lymph node dissection).
How the surgery is done
There are different surgery methods to remove the prostate:
| open radical prostatectomy | usually done through one long cut in the lower abdomen (belly) |
| laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (keyhole surgery) | small surgical instruments and a camera are inserted through several small cuts in the abdomen. The surgeon performs the procedure by moving the instruments using the image on the screen as a guide |
| robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy | laparoscopic surgery performed with help from a robotic system. The surgeon uses a 3D picture and control panel to move robotic arms holding instruments. |
Radical prostatectomy to remove the prostate
Making decisions about surgery
Talk to your surgeon about whether surgery or another treatment such as radiation therapy is the best option for you. Also ask what surgical methods are available to you. Ask about the advantages and disadvantages of each option. There may be extra costs involved for some procedures and they are not all available at every hospital. You may want to consider getting a second opinion about the most suitable type of surgery. See more about Making treatment decisions.
The surgeon’s experience and skill are more important than the type of surgery offered. Compared to open surgery, both standard laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgery usually mean a shorter stay in hospital, less bleeding, a smaller scar and a faster recovery. Current evidence suggests that the different approaches have a similar risk of side effects. Take the time you need to make the right decision for you.
For more on this, see our general section on Surgery.
→ READ MORE: What to expect after surgery
Podcast: Making Treatment Decisions
Listen to more episodes from our podcast for people affected by cancer
More resources
Prof Declan Murphy, Consultant Urologist, Director – Genitourinary Oncology, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre and The University of Melbourne, VIC; Alan Barlee, Consumer; Dr Patrick Bowden, Radiation Oncologist, Epworth Hospital, Richmond, VIC; Bob Carnaby, Consumer; Dr Megan Crumbaker, Medical Oncologist, St Vincent’s Hospital Sydney, NSW; Henry McGregor, Health Physiotherapist, Adelaide Men’s Health Physio, SA; Jessica Medd, Senior Clinical Psychologist, Department of Urology, Concord Repatriation General Hospital and Headway Health, NSW; Dr Gary Morrison, Shine a Light (LGBTQIA+ Cancer Support Group); Caitriona Nienaber, 13 11 20 Consultant, Cancer Council WA; Graham Rees, Consumer; Kerry Santoro, Prostate Cancer Specialist Nurse Consultant, Southern Adelaide Local Health Network, SA; Prof Phillip Stricker, Chairman, Department of Urology, St Vincent’s Private Hospital, NSW; Dr Sylvia van Dyk, Brachytherapy Lead, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, VIC.
View the Cancer Council NSW editorial policy.
View all publications or call 13 11 20 for free printed copies.



